Within the intricate workings of the human body, a symphony of interconnected structures orchestrates life’s processes. Among these essential components are organs and organ systems, each playing a distinct role in maintaining our health and well-being. While these terms may sound similar, they represent distinct levels of organization within the body’s structural hierarchy. Understanding the difference between organs and organ systems is fundamental to comprehending the body’s remarkable ability to function as a cohesive unit.
Delving into the World of Organs
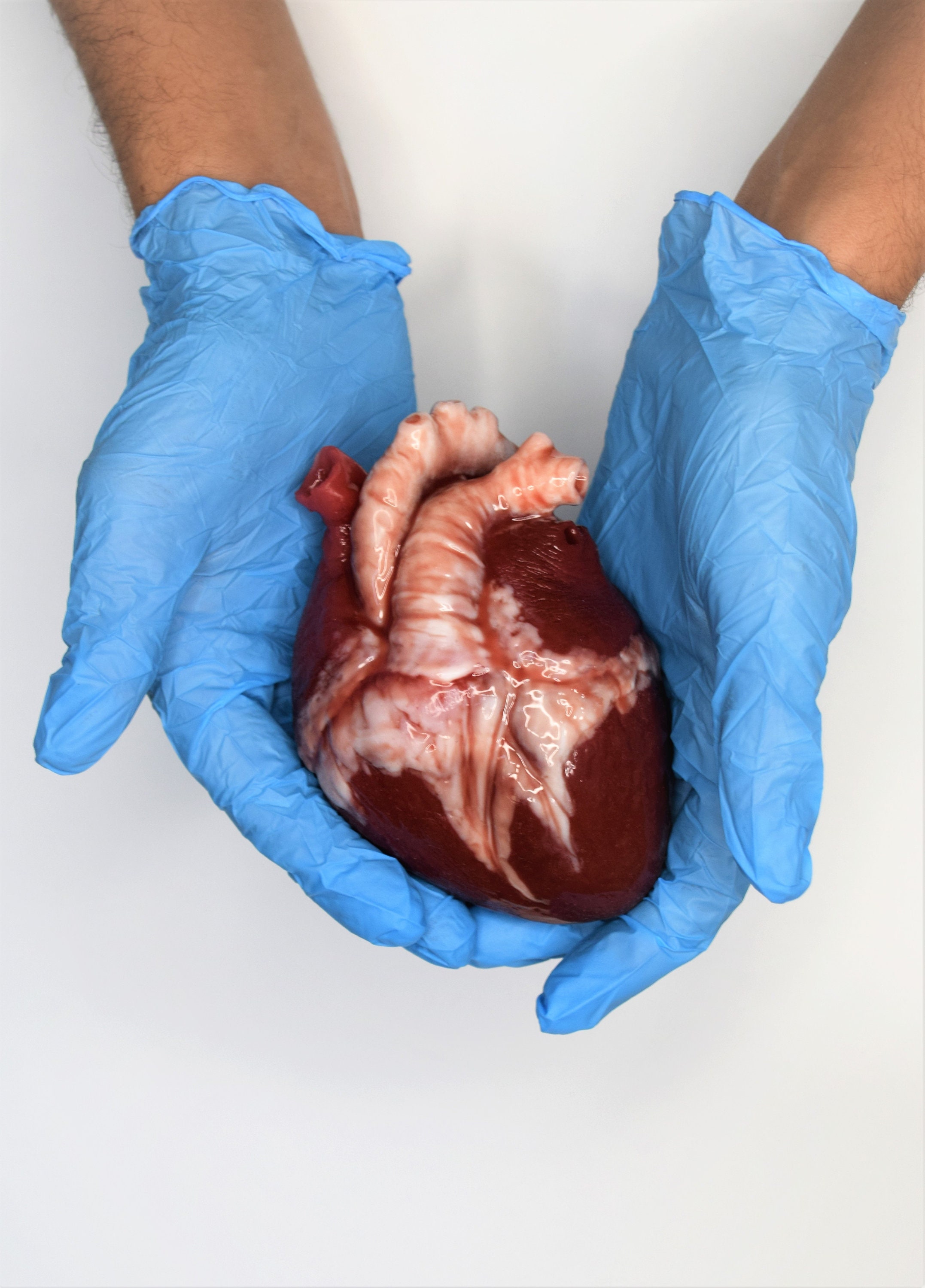
An organ is a collection of diverse tissues that work together to perform a specific function within the body. It is the culmination of multiple tissue types, each contributing specialized cells and structures to achieve a common goal. Organs are the building blocks of the body’s intricate machinery, each playing a vital role in maintaining homeostasis, the delicate balance that sustains life.
Consider the heart, the tireless pump that propels blood throughout the body. Its intricate network of muscles, valves, and blood vessels works in harmony to deliver oxygen and nutrients to every cell. The heart, as an organ, represents the collective effort of its constituent tissues, each performing a specialized task to ensure the smooth flow of life-sustaining blood.
Understanding Organ Systems

An organ system, a higher level of organization, comprises a group of organs that work together to carry out a broader physiological function. Each organ within the system contributes its unique expertise to achieve a common goal, creating a synergistic partnership that enhances the overall function.
The digestive system, a prime example of an organ system, orchestrates the complex process of breaking down food into its essential nutrients. Organs like the stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas work in concert, each performing specialized tasks like secretion, digestion, absorption, and elimination. The digestive system, as a whole, ensures that the body extracts the necessary sustenance from food, providing the building blocks for growth and repair.
Key Distinctions Between Organs and Organ Systems
The fundamental difference between organs and organ systems lies in their level of complexity and scope of function. Organs represent the basic functional units of the body, while organ systems encompass a broader network of organs working together to achieve a more elaborate physiological purpose.
Here’s a table summarizing the key distinctions between organs and organ systems:
| Feature | Organs | Organ Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Level of organization | Basic functional unit | Network of organs |
| Scope of function | Specific task | Broader physiological function |
| Complexity | Less complex | More complex |
| Example | Heart, stomach, lungs | Digestive system, circulatory system, nervous system |
Conclusion
Organs and organ systems, like the intricate gears of a finely tuned machine, work in harmony to sustain life. Organs, the fundamental building blocks, perform specialized tasks, while organ systems, the overarching frameworks, coordinate these efforts to achieve broader physiological functions. Understanding the intricate interplay between these structural levels is essential for appreciating the remarkable complexity and resilience of the human body.