In the realm of child health, the acronyms IYCF and IYCF-E frequently appear, often causing confusion among individuals seeking information about these crucial healthcare practices. While both abbreviations represent strategies for promoting optimal infant and young child feeding, they differ in their scope and applicability. Understanding the distinction between IYCF and IYCF-E is essential for ensuring the well-being of infants and young children, particularly in challenging environments.
Unveiling the Essence of IYCF
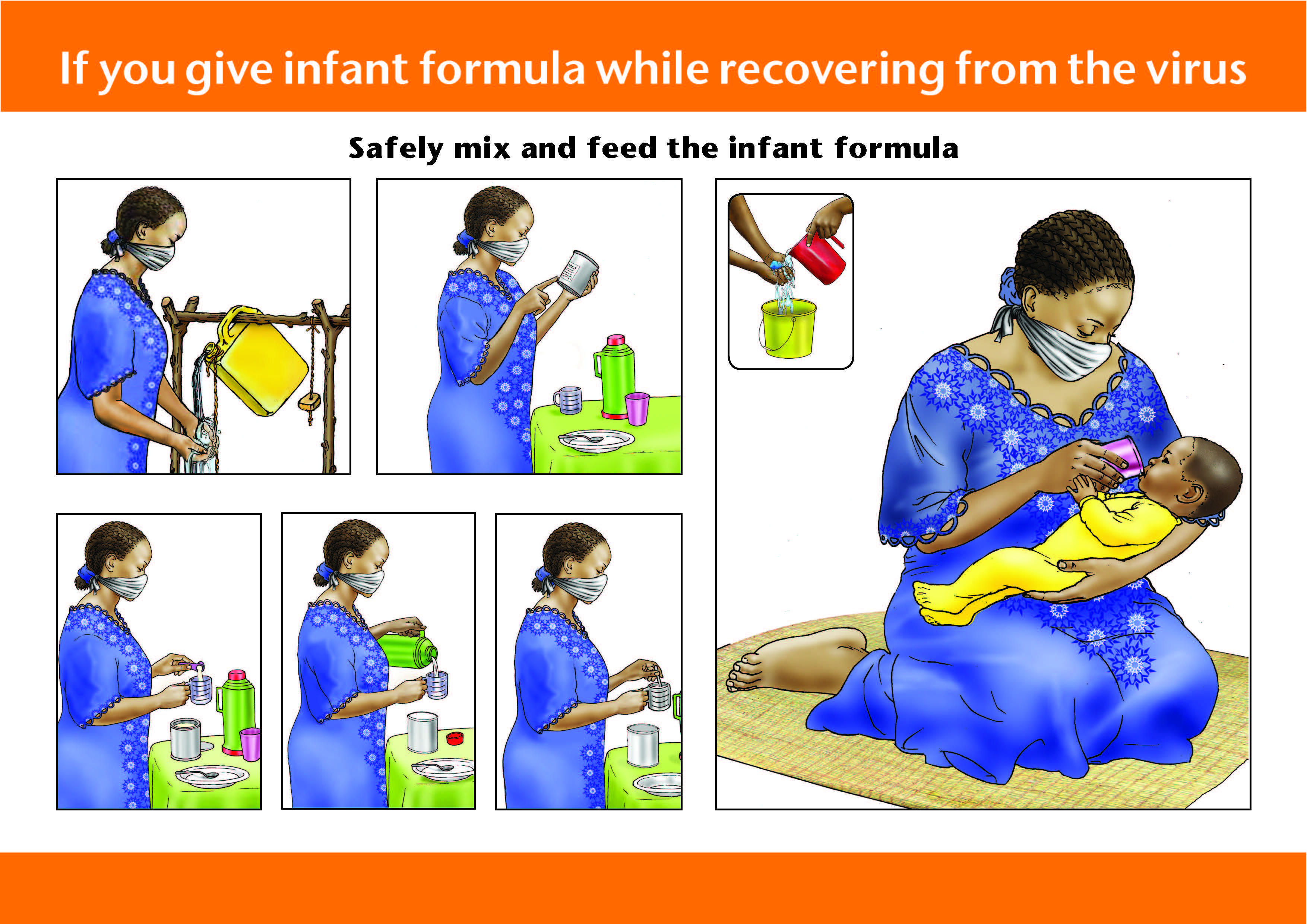
Infant and Young Child Feeding (IYCF) encompasses a set of recommendations and guidelines for promoting optimal feeding practices for infants and young children, covering the period from birth to two years of age. IYCF emphasizes the importance of exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life, followed by the introduction of safe and appropriate complementary foods alongside continued breastfeeding up to two years of age and beyond.
Key Principles of IYCF
Initiation of breastfeeding within one hour of birth: Early initiation promotes bonding, provides immediate nutrition, and protects against infections.
Exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months: Breast milk provides complete nutrition and protects against infections during this critical developmental period.
Continued breastfeeding alongside complementary foods: Breastfeeding remains an essential source of nutrients and antibodies beyond six months.
Introduction of safe and appropriate complementary foods: Introduce complementary foods at six months, ensuring they are age-appropriate, nutritious, and hygienically prepared.
IYCF-E: Addressing Feeding Challenges in Emergencies

Infant and Young Child Feeding in Emergencies (IYCF-E) extends the principles of IYCF to address the unique challenges of feeding infants and young children in humanitarian crises. Emergencies, such as natural disasters, conflicts, and displacement, can disrupt food supply chains, sanitation, and access to healthcare, putting infants and young children at increased risk of malnutrition and morbidity.
IYCF-E Strategies
Protect, support, and promote breastfeeding: Emphasize the importance of continued breastfeeding even in emergencies, providing support to mothers and addressing any breastfeeding challenges.
Ensure access to safe and appropriate complementary foods: Adapt feeding practices to the available resources, promoting locally available and culturally acceptable complementary foods.
Prevent and manage malnutrition: Implement monitoring and intervention strategies to identify and address malnutrition in infants and young children.
Comparative Table
| Feature | IYCF | IYCF-E |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | General guidelines for optimal infant and young child feeding | Tailored strategies for feeding infants and young children in emergencies |
| Primary focus | Promoting exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months and continued breastfeeding beyond | Protecting, supporting, and promoting breastfeeding in challenging environments |
| Additional considerations | Introduction of safe and appropriate complementary foods | Ensuring access to safe and appropriate complementary foods in emergencies |
| Addressing malnutrition | General recommendations for prevention and management | Specific strategies for preventing and managing malnutrition in emergencies |
Conclusion
IYCF and IYCF-E represent crucial approaches to ensuring optimal infant and young child feeding, promoting their health, growth, and development. IYCF provides a comprehensive framework for feeding practices under normal circumstances, while IYCF-E adapts these principles to address the unique challenges of feeding infants and young children in emergencies. Understanding the distinction between these two strategies empowers individuals and organizations to effectively support and protect the nutritional well-being of infants and young children in diverse settings.