In the realm of women’s health, urinary tract infections (UTIs) and sexually transmitted infections (STDs) are two prevalent conditions that often cause confusion and concern. While both acronyms represent infections that can affect the urinary tract, they differ in their causes, modes of transmission, and treatment approaches. Understanding the distinction between UTIs and STDs is crucial for seeking appropriate medical attention and preventing further complications.
UTI: A Microbial Intruder in the Urinary Tract
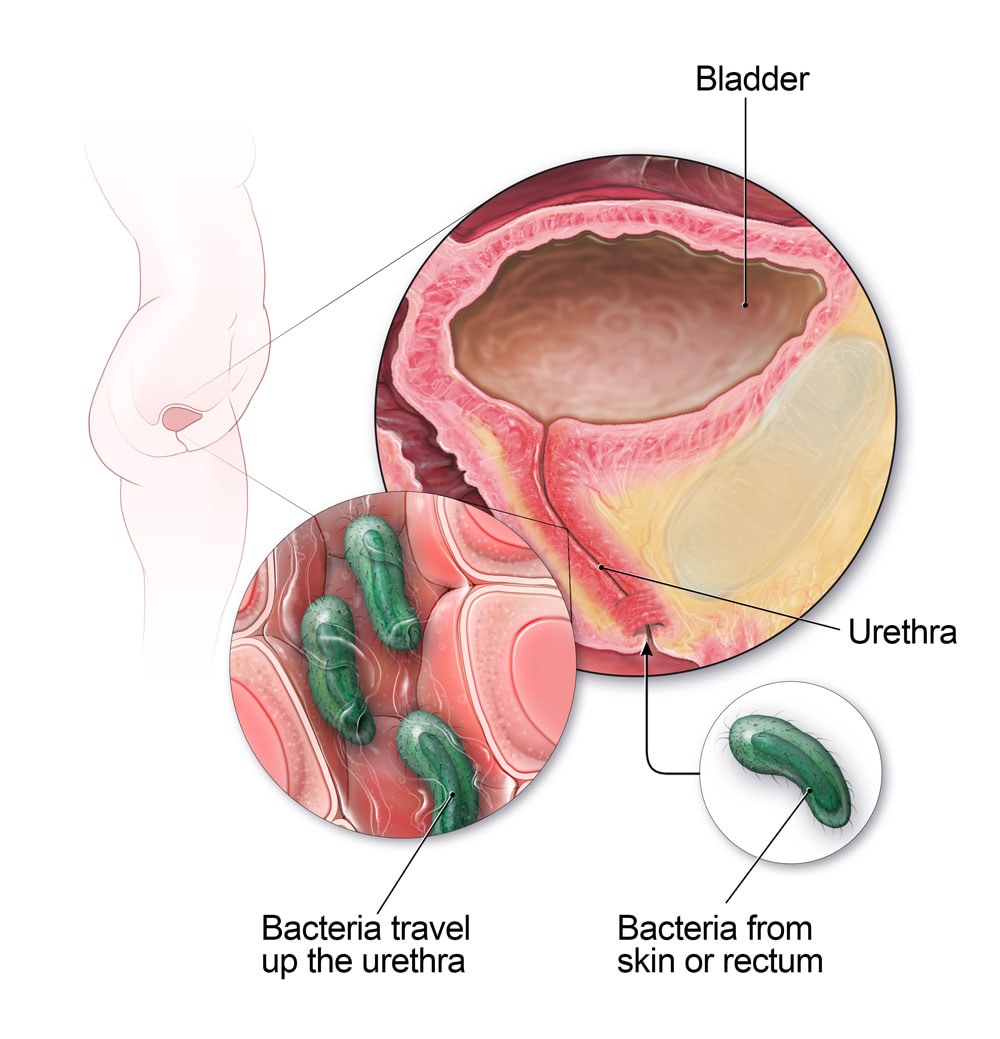
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection caused by the presence and growth of microorganisms, typically bacteria, in any part of the urinary tract, including the urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys. UTIs are more common in women due to their shorter urethras, which provide a shorter pathway for bacteria to enter the bladder.
Key Characteristics of UTIs
- Causes: Bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract or skin entering the urethra and colonizing the urinary tract
- Symptoms: Burning sensation during urination, frequent urination, urgency to urinate, cloudy, dark, or strong-smelling urine, pelvic pain or pressure, and in severe cases, blood in the urine
- Treatment: Antibiotics to eradicate the infection
STD: A Spectrum of Infections Transmitted through Sexual Contact

Sexually transmitted infections (STDs) are a group of infections that are transmitted from one person to another through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. STDs are caused by a variety of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
Commonly Encountered STDs
- Chlamydia: A bacterial infection that can cause inflammation and discharge in the genitals
- Gonorrhea: A bacterial infection that can cause pain and discharge in the genitals
- Trichomoniasis: A parasitic infection that causes itching and discharge in the genitals
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV): A viral infection that causes painful blisters or sores on the genitals or around the mouth
- Human papillomavirus (HPV): A viral infection that can cause warts on the genitals, mouth, or throat, and is associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer
Distinguishing UTIs from STDs
While UTIs and STDs share some common symptoms, such as burning sensation during urination and frequent urination, they differ in their causes, modes of transmission, and treatment approaches.
| Feature | UTI | STD |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Bacterial infection of the urinary tract | Infection caused by a variety of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites |
| Transmission | Not typically transmitted through sexual contact | Transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex |
| Treatment | Antibiotics | Varies depending on the specific STD, but may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, or antiparasitic drugs |
Seeking Medical Attention
If you are experiencing any symptoms of a UTI or STD, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent further complications and promote faster recovery.
Preventive Measures
While UTIs and STDs cannot be completely prevented, there are several measures you can take to reduce your risk of contracting these infections:
UTI Prevention: Practice good hygiene, keep the genital area clean and dry, drink plenty of fluids, empty your bladder regularly, and avoid using douches or scented soaps.
STD Prevention: Practice safe sex by using condoms consistently and correctly, avoid sharing needles, and get tested for STDs regularly.
Conclusion
UTIs and STDs are two common conditions that affect women’s health. Understanding the distinction between these infections is essential for recognizing symptoms, seeking appropriate medical care, and implementing preventive measures. By taking proactive steps to maintain good hygiene, practicing safe sex, and undergoing regular screenings, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting UTIs and STDs.