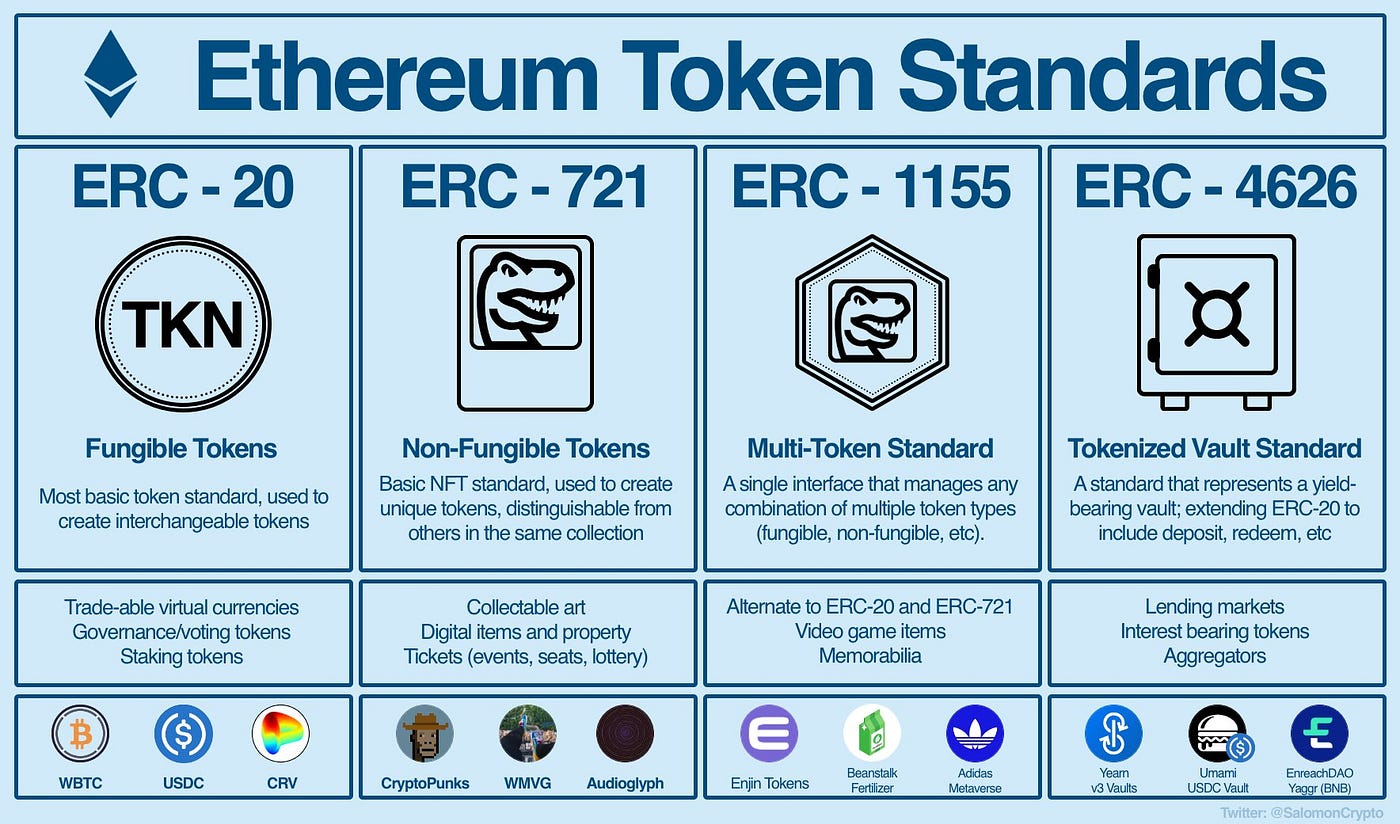
In the realm of blockchain technology, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have emerged as revolutionary digital assets, representing ownership and authenticity of unique digital items. Among the diverse NFT standards, ERC-721 and ERC-1155 stand out as two prominent and widely adopted standards. While both facilitate the creation and management of NFTs, they differ in their capabilities and applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of ERC-721 and ERC-1155, elucidating their key distinctions, operational mechanisms, and suitability for different use cases.
ERC-721: The Pioneer of Non-Fungible Tokens
ERC-721, introduced in 2018, revolutionized the NFT landscape by establishing a standard for representing and managing truly unique digital assets. Each ERC-721 token is non-fungible, meaning it is irreplaceable and holds a distinct identity, analogous to a physical collectible item. This characteristic makes ERC-721 ideal for representing digital collectibles, such as artwork, game items, and virtual land parcels.
Operational Mechanism of ERC-721:
Token Creation: ERC-721 tokens are minted on the Ethereum blockchain, assigning each token a unique identifier.
Ownership Tracking: The ownership of each ERC-721 token is tracked on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and immutability.
Transferable Assets: ERC-721 tokens can be transferred between owners, facilitating ownership changes and transactions.
Applications of ERC-721:
Digital collectibles: Artwork, game items, music tracks, virtual land parcels, and other unique digital assets.
Identity management: Secure storage and verification of digital identities, certificates, and credentials.
Supply chain tracking: Tracking the origin and ownership of physical assets linked to NFTs.
ERC-1155: Expanding the NFT Horizon
ERC-1155, introduced in 2019, emerged as an extension of ERC-721, offering enhanced flexibility and versatility in managing both fungible and non-fungible tokens. ERC-1155 enables the creation of contracts that can manage multiple token types within a single smart contract, making it more efficient and cost-effective.

Operational Mechanism of ERC-1155:
Multi-Token Management: ERC-1155 contracts can manage multiple token types, including fungible tokens, semi-fungible tokens, and non-fungible tokens.
Batch Transfers: ERC-1155 allows for efficient batch transfers of multiple token types, reducing transaction costs.
Dynamic Metadata: ERC-1155 supports dynamic metadata, enabling customization of token properties and attributes.
Applications of ERC-1155:
Game assets: Managing in-game items, currencies, and collectibles within a single contract.
Supply chain management: Tracking the movement and ownership of physical assets linked to NFTs.
Ticketing and membership: Issuing unique tickets, memberships, and access tokens.
ERC-721 vs. ERC-1155: A Comparative Glance
| Feature | ERC-721 | ERC-1155 |
|---|---|---|
| Primary focus | Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) | Fungible, semi-fungible, and non-fungible tokens |
| Token types | Single token type per contract | Multiple token types per contract |
| Transfer efficiency | Less efficient for batch transfers | Efficient for batch transfers |
| Metadata | Static metadata | Dynamic metadata |
| Applications | Digital collectibles, identity management, supply chain tracking | Game assets, supply chain management, ticketing and membership |
Conclusion: Choosing the Right NFT Standard
The choice between ERC-721 and ERC-1155 depends on the specific requirements of the project or use case. For projects that solely involve non-fungible tokens and require a focus on unique digital collectibles, ERC-721 remains a robust and well-established standard. However, for projects that demand more flexibility and efficiency in managing multiple token types, ERC-1155 offers a compelling solution.
In conclusion, ERC-721 and ERC-1155 have revolutionized the NFT landscape, providing developers and creators with powerful tools to represent and manage digital assets. By understanding the nuances of each standard, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions about which