
In the realm of electronics, surface-mount devices (SMDs) have become increasingly prevalent due to their compact size, high performance, and suitability for automated assembly. Among the diverse array of SMD components, capacitors and resistors stand out as fundamental elements in electronic circuits. While both play essential roles in circuit design, they differ in their functions, characteristics, and applications.
Capacitors: Storing and Releasing Electrical Energy
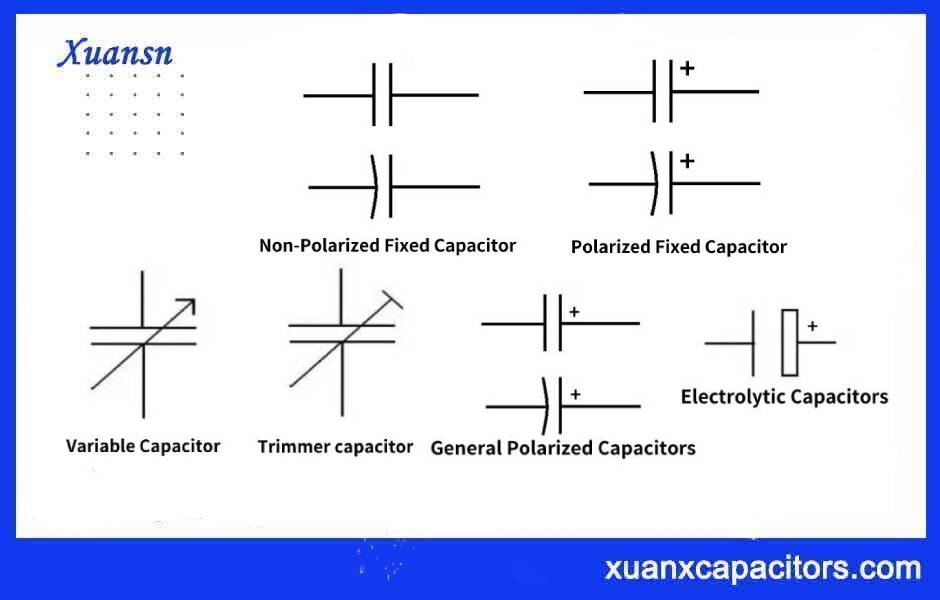
Capacitors are passive electronic components that store electrical energy in the form of an electric field. They are composed of two or more conductive plates separated by an insulating material, known as a dielectric. When a voltage is applied across the plates, an electric charge is stored within the dielectric. The amount of charge that can be stored depends on the capacitance of the capacitor, measured in farads (F).
Capacitors are used in a wide range of electronic circuits, including:
Filtering: Capacitors can filter out unwanted noise and ripples from power supplies, ensuring a clean and stable voltage source.
Timing: Capacitors can control the timing of electronic circuits, such as oscillators and timers.
Coupling: Capacitors can couple different stages of an electronic circuit, allowing signals to pass while blocking direct current (DC).
Resistors: Opposing the Flow of Electric Current

Resistors are passive electronic components that impede the flow of electric current. They are made of conductive materials, such as carbon or metal alloys, and are designed to dissipate electrical energy as heat. The resistance of a resistor, measured in ohms (Ω), determines the amount of current it opposes.
Resistors are used in a wide range of electronic circuits, including:
Current limiting: Resistors can limit the current flowing through a circuit, protecting components from damage caused by excessive current.
Voltage division: Resistors can divide a voltage into smaller proportional voltages, enabling precise voltage adjustments.
Load matching: Resistors can match the impedance of different circuit components, ensuring efficient signal transfer and preventing reflections.
Key Differences between SMD Capacitors and Resistors
The table below summarizes the key differences between SMD capacitors and resistors:
| Feature | SMD Capacitors | SMD Resistors |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Stores electrical energy | Opposes the flow of electric current |
| Symbol | ||
| Unit of measurement | Farads (F) | Ohms (Ω) |
| Primary applications | Filtering, timing, coupling | Current limiting, voltage division, load matching |
| Electrical properties | Capacitance, dielectric constant | Resistance, resistivity |
Choosing the Right SMD Component
The selection between SMD capacitors and resistors depends on the specific function and requirements of the electronic circuit:
SMD Capacitors: Used for storing and releasing electrical energy, filtering out noise, timing circuits, and coupling different stages of circuits.
SMD Resistors: Used for limiting current flow, dividing voltage, matching impedance, and dissipating electrical energy as heat.
Conclusion
SMD capacitors and resistors are fundamental building blocks in electronic circuits, each playing a distinct role in shaping the behavior of electrical signals. By understanding their unique properties and applications, engineers and hobbyists can effectively utilize these SMD components to design and build a wide range of electronic devices. Whether filtering out noise, controlling current flow, or timing circuit operations, SMD capacitors and resistors remain indispensable tools in the world of electronics.