Unveiling the Distinctions between Thin Layer Chromatography and High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatography
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) and high-performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) are analytical techniques used to separate and identify components of a mixture. Both methods utilize a stationary phase, typically a thin layer of adsorbent material coated on a plate, and a mobile phase, a solvent or solvent system, to achieve separation. However, HPTLC is an advanced form of TLC that offers enhanced separation efficiency, resolution, and sensitivity.
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
TLC is a versatile and widely used chromatographic technique due to its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of operation. It involves applying a sample solution to a TLC plate, placing the plate in a developing chamber containing the mobile phase, and allowing the mobile phase to travel up the plate. As the mobile phase moves, it carries the sample components at different rates based on their affinity for the stationary phase. This separation results in distinct bands or spots on the plate, representing the individual components of the mixture.
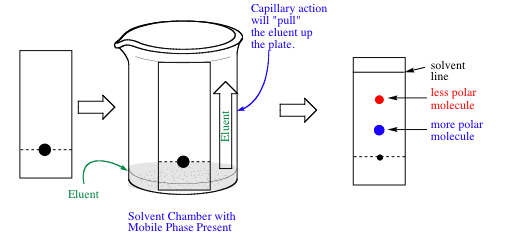
Key Features of TLC:
- Simple and inexpensive technique
- Easy to set up and operate
- Suitable for a wide range of samples
- Provides qualitative and semi-quantitative analysis
High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC)
HPTLC is an advanced form of TLC that employs high-performance stationary phases and optimized developing chambers to achieve enhanced separation efficiency and resolution. It also utilizes smaller adsorbent particles, resulting in narrower and more distinct bands on the plate. HPTLC offers improved sensitivity, enabling the detection of trace amounts of sample components.

Key Features of HPTLC:
- Enhanced separation efficiency and resolution
- Improved sensitivity for trace analysis
- Suitable for quantitative analysis
- Reproducible and reliable results
Comparing TLC and HPTLC
| Feature | TLC | HPTLC |
|---|---|---|
| Stationary Phase | Typical adsorbents like silica gel, alumina | High-performance adsorbents with smaller particle size |
| Developing Chamber | Simple chambers | Optimized chambers with controlled temperature and humidity |
| Separation Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Resolution | Lower | Higher |
| Sensitivity | Lower | Higher |
| Quantitation | Semi-quantitative | Quantitative |
| Reproducibility | Lower | Higher |
Applications of TLC and HPTLC
TLC and HPTLC have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Chemistry: Identifying and characterizing organic compounds
- Pharmaceuticals: Purity assessment of drugs and drug formulations
- Food Science: Analyzing food additives and contaminants
- Environmental Science: Monitoring environmental pollutants
- Forensic Science: Identifying substances in criminal investigations
Choosing Between TLC and HPTLC
The choice between TLC and HPTLC depends on the specific requirements of the analysis. TLC is a suitable choice for qualitative and semi-quantitative analysis when cost-effectiveness and simplicity are priorities. HPTLC is preferred for quantitative analysis, high-resolution separations, and trace detection.
Conclusion
TLC and HPTLC are valuable analytical tools for separating and identifying components of mixtures. TLC offers a simple and cost-effective approach for qualitative and semi-quantitative analysis, while HPTLC provides enhanced separation efficiency, resolution, and sensitivity for quantitative analysis and trace detection. Understanding the key differences between these techniques enables researchers and analysts to select the most appropriate method for their specific needs and achieve reliable results.