In the realm of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) technology, the terms VRV and VRF are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion among individuals seeking to understand these sophisticated systems. While both VRV and VRF represent advanced HVAC technologies, they exhibit distinct characteristics and applications. Delving into the nuances of VRV and VRF is crucial for making informed decisions when selecting an HVAC system for residential, commercial, or industrial settings.
VRV: The Pioneer of Variable Refrigerant Flow
VRV, or Variable Refrigerant Volume, stands as a pioneering HVAC technology developed by Daikin Industries, Ltd., in 1982. It revolutionized the HVAC industry by introducing the concept of variable refrigerant flow, a mechanism that efficiently controls the refrigerant flow to each indoor unit based on individual heating or cooling demands.
Key Features of VRV:
Variable Refrigerant Flow: VRV systems utilize variable refrigerant flow to optimize energy consumption and provide zone-specific comfort.
Individualized Control: Each indoor unit in a VRV system can be controlled independently, ensuring precise temperature regulation in different zones.
High Efficiency: VRV systems are known for their high energy efficiency, reducing operating costs and environmental impact.
Applications: VRV systems are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, providing versatile climate control solutions.
VRF: A Descendant of VRV Technology
VRF, or Variable Refrigerant Flow, is a term often used to describe HVAC systems that operate on the same principles as VRV technology but are manufactured by companies other than Daikin Industries. While these systems share the core concept of variable refrigerant flow, they may exhibit slight variations in design, features, and performance.
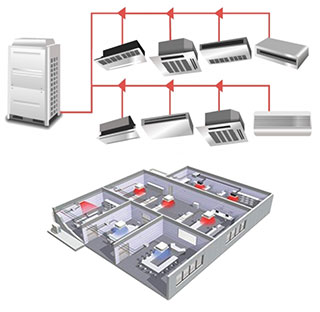
Key Features of VRF:
Variable Refrigerant Flow: VRF systems utilize variable refrigerant flow to optimize energy consumption and provide zone-specific comfort.
Individualized Control: Each indoor unit in a VRF system can be controlled independently, ensuring precise temperature regulation in different zones.
Diverse Manufacturer Options: VRF systems are available from a range of manufacturers, offering a variety of options and price points.
Applications: VRF systems are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, providing versatile climate control solutions.
Comparing VRV and VRF: A Side-by-Side Analysis
The table below summarizes the key differences between VRV and VRF:
| Feature | VRV | VRF |
|---|---|---|
| Originator | Daikin Industries, Ltd. | Various manufacturers |
| Trademark | Registered trademark of Daikin Industries | Generic term for variable refrigerant flow systems |
| Design | May exhibit slight variations in design compared to original VRV systems | Adheres to the core principles of variable refrigerant flow |
| Performance | High energy efficiency and reliable performance | Varies by manufacturer |
| Applications | Widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings | Widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings |
Conclusion: Embracing Efficient and Versatile HVAC Solutions
VRV and VRF systems represent significant advancements in HVAC technology, offering efficient, versatile, and zone-specific climate control solutions for a wide range of applications. Understanding the nuances of VRV and VRF empowers individuals to make informed decisions when selecting an HVAC system tailored to their specific needs and preferences. As HVAC technology continues to evolve, let us embrace innovation and strive for sustainable and energy-efficient climate control solutions for the future.
